Interactive Demo
A small gray rubber cube a small purple metal cube
A maple wood cabinet a blue fabric couch

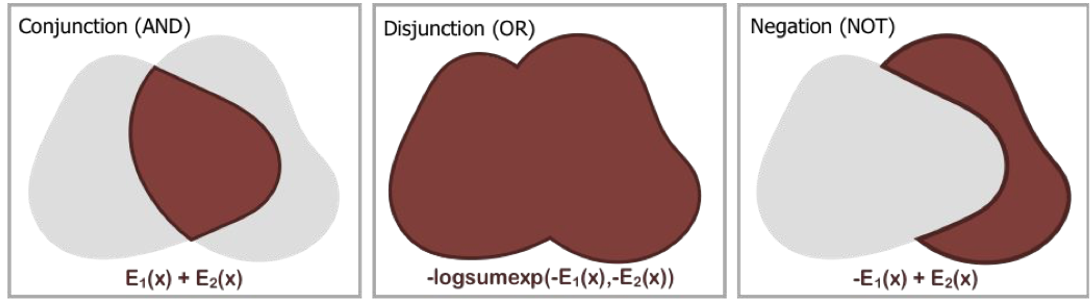
Learning to Compose Visual Relations
NeurIPS 2021 (Spotlight)
Nan Liu1* Shuang Li2* Yilun Du2* Joshua B. Tenenbaum2 Antonio Torralba2 (* indicate equal contribution)

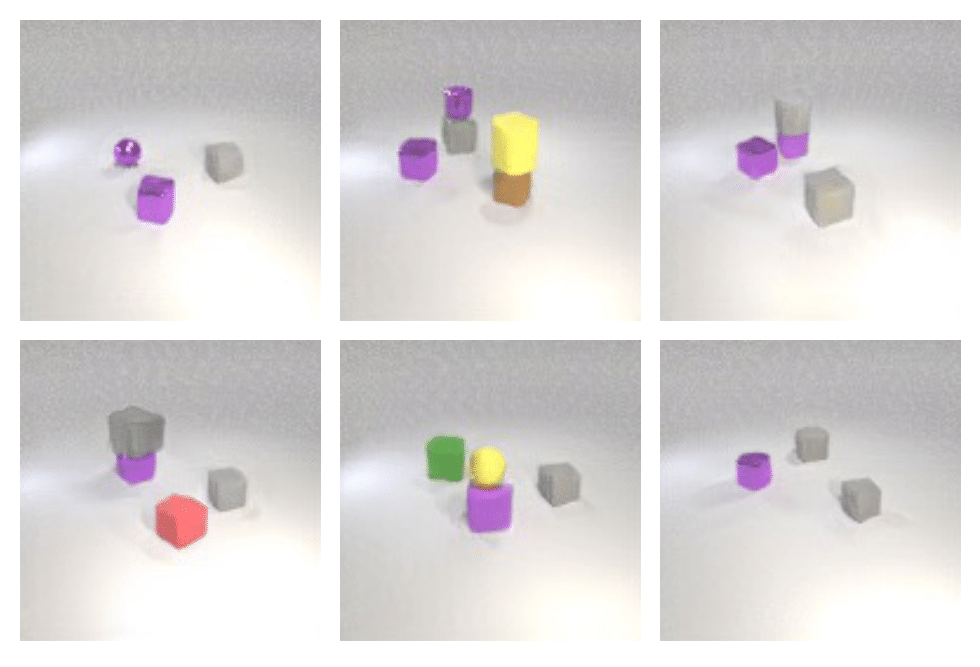
Image generation results on the CLEVR dataset. Image are generated based on 1 - 4 relational descriptions. Note that the models are trained on a single relational description and the composed scene relations (2, 3, and 4 relational descriptions) are outside the training distribution.
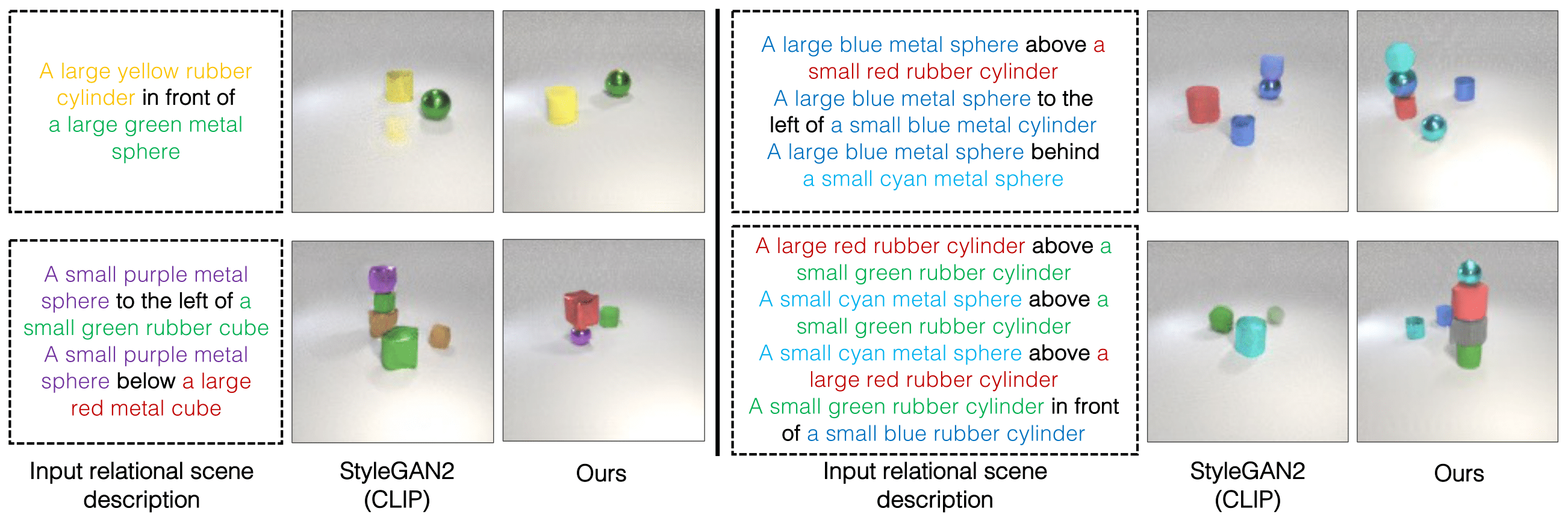
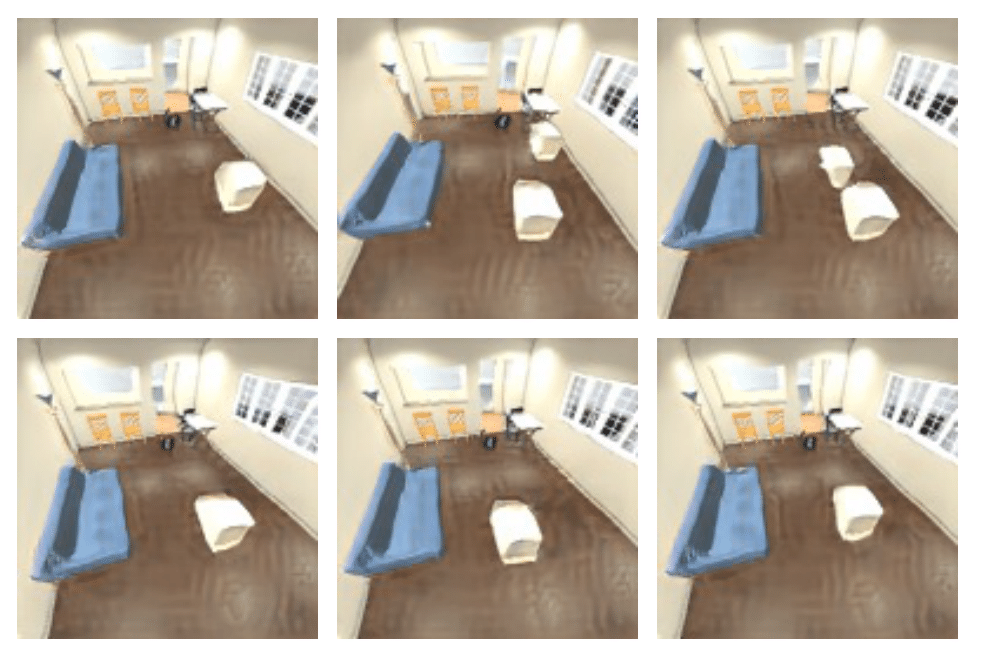
Image generation results on the iGibson dataset. Below are generated iGibson images. Note that the models are trained on a single relational description and the composed scene relations (2 relational descriptions) are outside the training distribution.
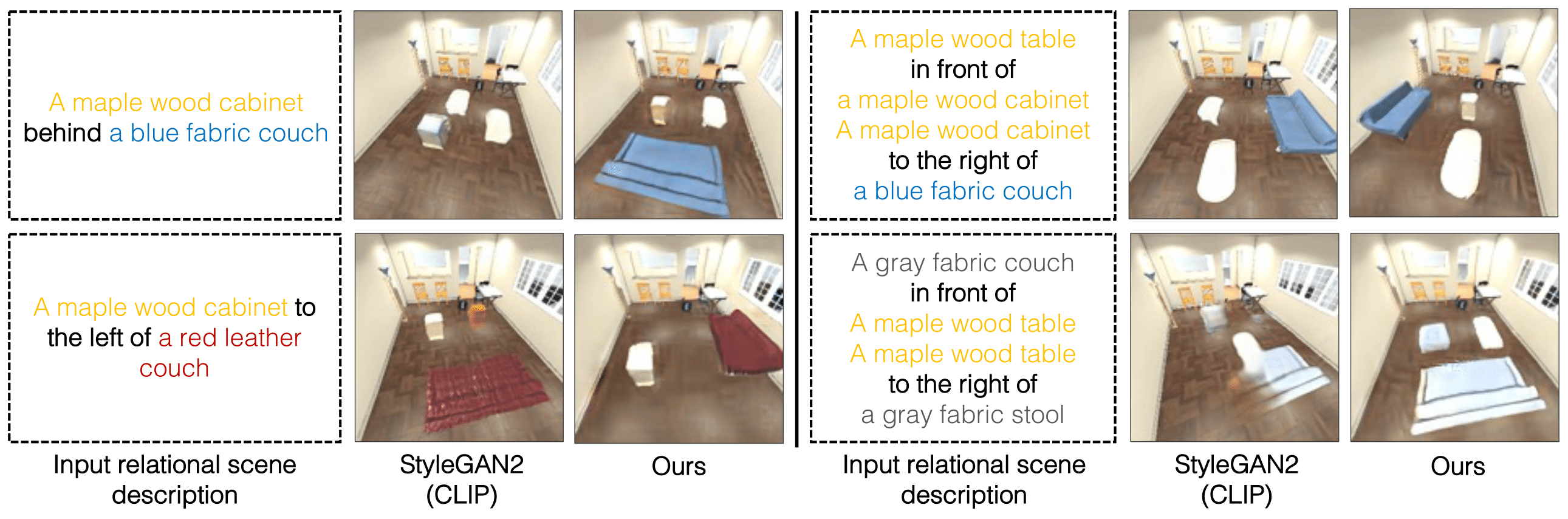
Image generation results on the real world Blocks dataset. Note that the models are trained on a single relational description and the composed scene relations (2 and 3 relational descriptions) are outside the training distribution.
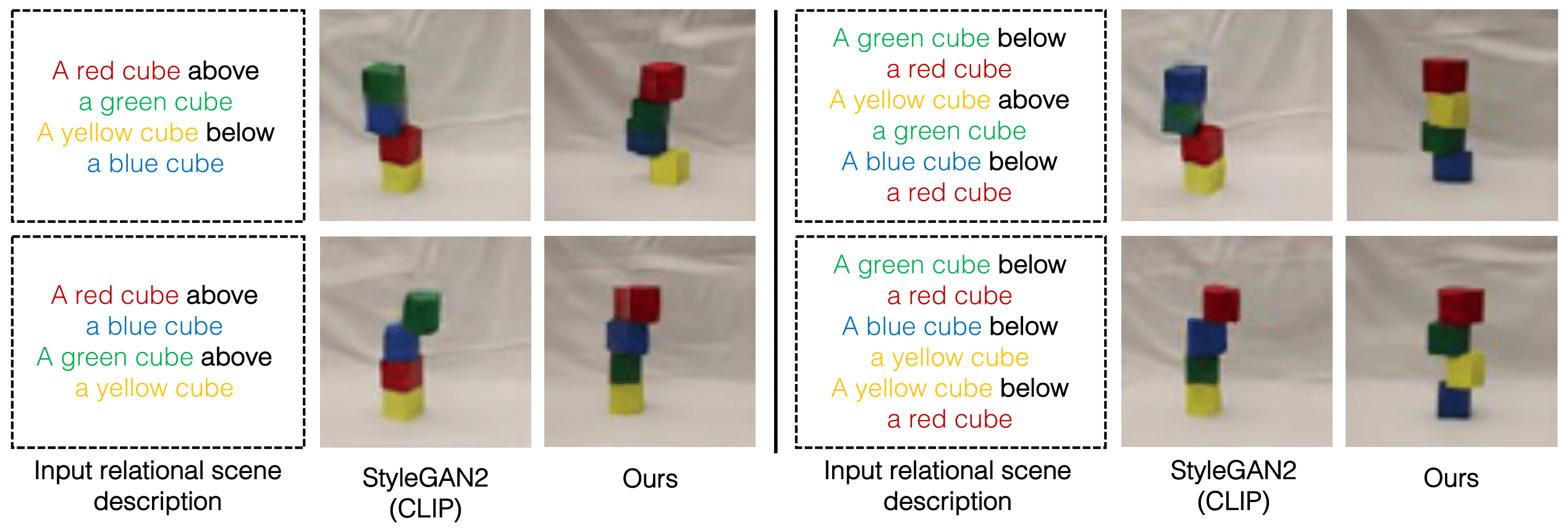
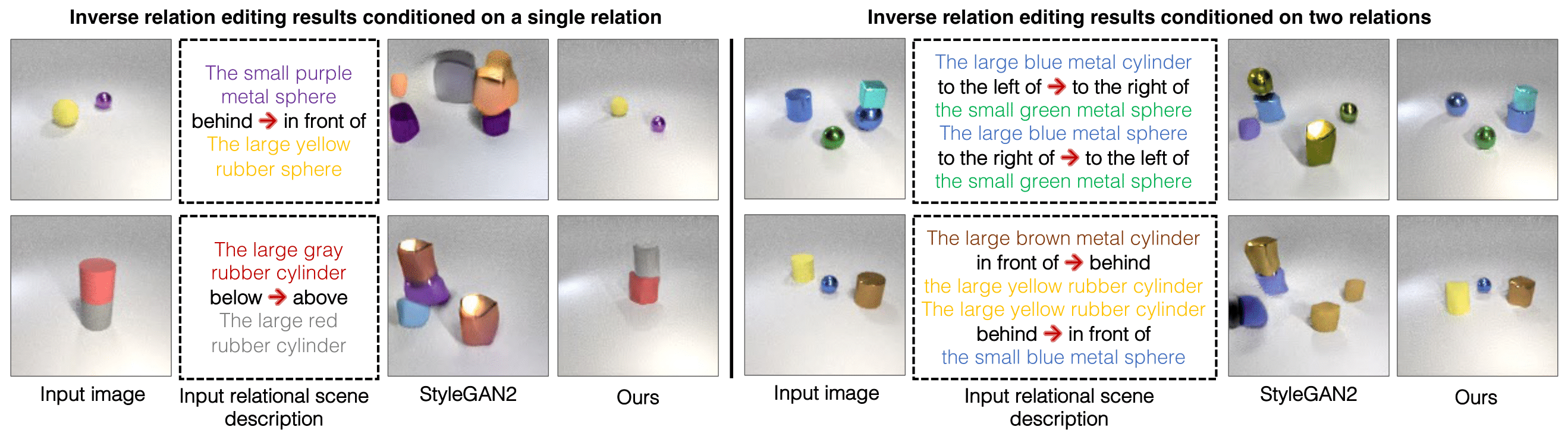
Image editing results on the CLEVR dataset. Left: image editing results based on a single relational scene description. Right: image editing results based on two composed relational scene descriptions. Note that the composed scene relations in the right part are outside the training distribution and our approach can still edit the images accurately.
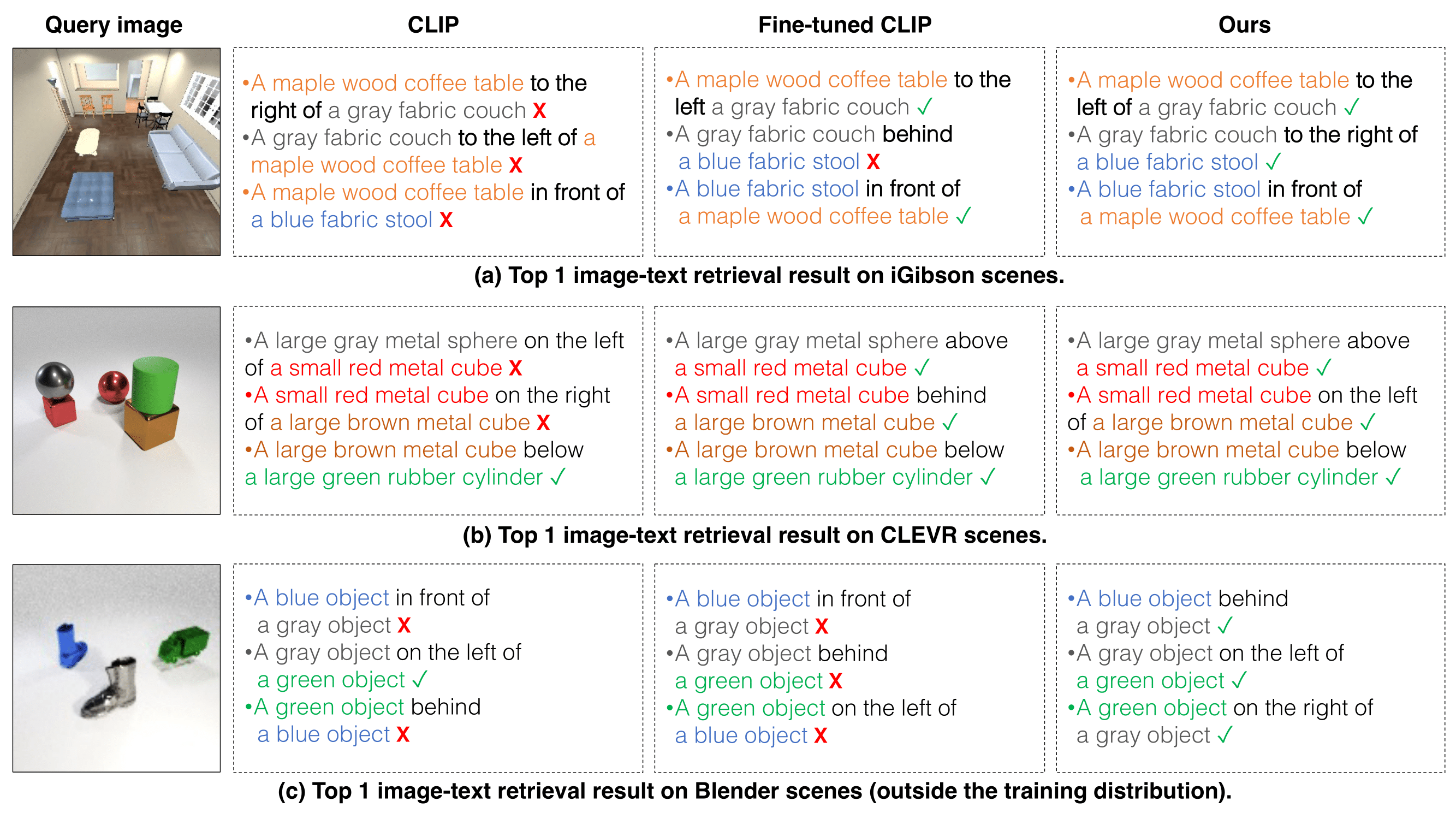
We evaluate whether our proposed model can understand different relational scene descriptions by image-to-text retrieval. We compare the proposed approach with the pretrained CLIP and fine-tuned CLIP and show their top-1 retrieved relation description based on the given image query.
Check out our related projects on compositional energy functions!